ThreadLocal字面上的意思是局部线程变量,每个线程通过ThreadLocal的get和set方法来访问和修改线程自己独有的变量。简单地说,ThreadLocal的作用就是为每一个线程提供了一个独立的变量副本,每一个线程都可以独立地改变自己的副本,而不会影响其它线程所对应的副本。
ThreadLocal的基本使用
ThreadLocal是一个泛型类,在创建的时候需要指定变量的类型:
1
| private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
|
ThreadLocal提供了set方法来设置变量的值,get方法获取变量的值,remove方法移除变量:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class ThreadLocalTest {
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
threadLocal.set("mrbird");
System.out.println(threadLocal.get());
threadLocal.remove();
System.out.println(threadLocal.get());
}
}
|
程序输出如下:
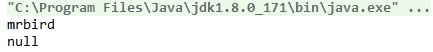
我们也可以给ThreadLocal设置初始值,设置初始值有两种方式:
- 重写
initialValue方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class ThreadLocalTest {
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<String>(){
@Override
protected String initialValue() {
return "初始值";
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(threadLocal.get());
}
}
|
- 使用ThreadLocal的
withInitial方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public class ThreadLocalTest {
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> "初始值");
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(threadLocal.get());
}
}
|
值得注意的是remove无法移除初始值:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public class ThreadLocalTest {
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> "初始值");
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
threadLocal.remove();
System.out.println(threadLocal.get());
}
}
|
演示多线程间独立
在多个线程中使用ThreadLocal:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| public class ThreadLocalTest2 {
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
private static Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
threadLocal.set("thread t1");
try {
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(random.nextInt(1000));
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + threadLocal.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "thread1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
threadLocal.set("thread t2");
try {
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(random.nextInt(1000));
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + threadLocal.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "thread2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + threadLocal.get());
}
}
|
程序输出如下:

结果证明了ThreadLocal在每个线程间是相互独立的,threadLocal在thread1、thread2和main线程间都有一份独立拷贝。
ThreadLocal基本原理
在ThreadLocal类中有一个静态内部类ThreadLocalMap(概念上类似于Map),用键值对的形式存储每一个线程的变量副本,ThreadLocalMap中元素的key为当前ThreadLocal对象,而value对应线程的变量副本。
我们使用Map来代替ThreadLocalMap,创建一个简易的类ThreadLocal实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public class MyThreadLocal<T> {
private final Map<Thread, T> threadLocalMap = new HashMap<>();
public void set(T t) {
synchronized (this) {
Thread key = Thread.currentThread();
threadLocalMap.put(key, t);
}
}
public T get() {
synchronized (this) {
Thread key = Thread.currentThread();
T t = threadLocalMap.get(key);
if (t == null) {
return initalValue();
} else {
return t;
}
}
}
public T initalValue() {
return null;
}
}
|
使用方式和之前的例子一致:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| public class ThreadLocalTest3 {
private static MyThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new MyThreadLocal<String>() {
@Override
public String initalValue() {
return "initalValue";
}
};
private static Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
threadLocal.set("thread t1");
try {
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(random.nextInt(1000));
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + threadLocal.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "thread1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
threadLocal.set("thread t2");
try {
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(random.nextInt(1000));
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + threadLocal.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "thread2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + threadLocal.get());
}
}
|
程序输出如下:

使用建议
- 将ThreadLocal变量指定为
private static;
- 使用完毕后显式地调用
remove方法移除。


